毕业设计—基于Python的搜索引擎实现!毕设都这么容易吗?
前言
1.实现
1.1 系统架构
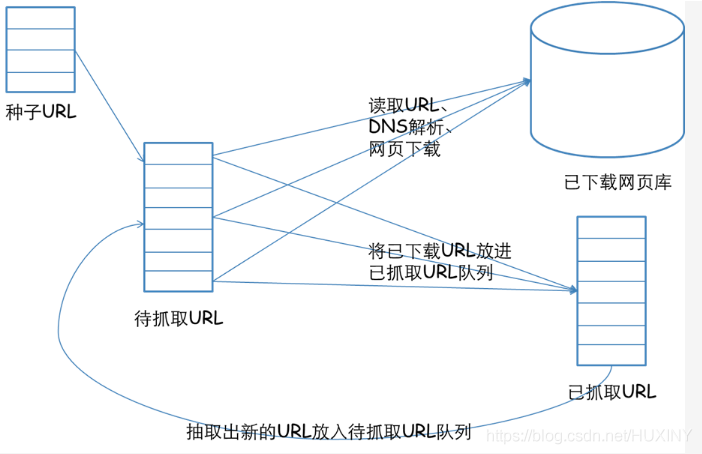
信息采集模块
信息处理模块
建立索引模块
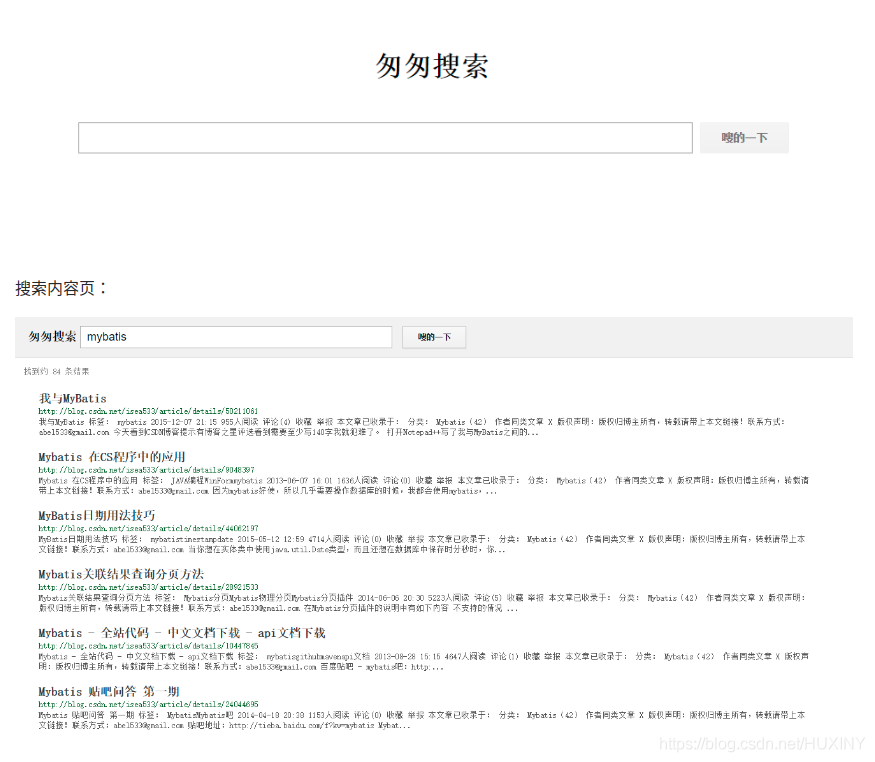
查询和 web 交互模块
爬取数据
中文分词
相关度排序
建立web交互。
1.2 爬取大量网页数据
# encoding=utf-8
# 导入爬虫包
from selenium import webdriver
# 睡眠时间
import time
import re
import os
import requests
# 打开编码方式utf-8打开
# 睡眠时间 传入int为休息时间,页面加载和网速的原因 需要给网页加载页面元素的时间
def s(int):
time.sleep(int)
# html/body/div[1]/table/tbody/tr[2]/td[1]/input
# http://dmfy.emindsoft.com.cn/common/toDoubleexamp.do
if __name__ == '__main__':
#查询的文件位置
# fR = open('D: est.txt','r',encoding = 'utf-8')
# 模拟浏览器,使用谷歌浏览器,将chromedriver.exe复制到谷歌浏览器的文件夹内
chromedriver = r"C:UserszhaofahuAppDataLocalGoogleChromeApplicationchromedriver.exe"
# 设置浏览器
os.environ["webdriver.chrome.driver"] = chromedriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome(chromedriver)
# 最大化窗口 用不用都行
browser.maximize_window()
# header = {'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.100 Safari/537.36'}
# 要爬取的网页
neirongs = [] # 网页内容
response = [] # 网页数据
travel_urls = []
urls = []
titles = []
writefile = open("docs.txt", 'w', encoding='UTF-8')
url = 'http://travel.yunnan.cn/yjgl/index.shtml'
# 第一页
browser.get(url)
response.append(browser.page_source)
# 休息时间
s(3)
# 第二页的网页数据
#browser.find_element_by_xpath('// *[ @ id = "downpage"]').click()
#s(3)
#response.append(browser.page_source)
#s(3)
# 第三页的网页数据
#browser.find_element_by_xpath('// *[ @ id = "downpage"]').click()
#s(3)
#response.append(browser.page_source)
# 3.用正则表达式来删选数据
reg = r'href="(//travel.yunnan.cn/system.*?)"'
# 从数据里爬取data。。。
# 。travel_urls 旅游信息网址
for i in range(len(response)):
travel_urls = re.findall(reg, response[i])
# 打印出来放在一个列表里
for i in range(len(travel_urls)):
url1 = 'http:' + travel_urls[i]
urls.append(url1)
browser.get(url1)
content = browser.find_element_by_xpath('/html/body/div[7]/div[1]/div[3]').text
# 获取标题作为文件名
b = browser.page_source
travel_name = browser.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="layer213"]').text
titles.append(travel_name)
print(titles)
print(urls)
for j in range(len(titles)):
writefile.write(str(j) + ' ' + titles[j] + ' ' + str(urls[j])+'
')
s(1)
browser.close()1.3 中文分词
1.4 相关度排序
第1个排名算法:根据单词位置进行评分的函数
# 根据单词位置进行评分的函数. # rows是[(urlid1,wordlocation1_1,wordlocation1_2,wordlocation1_3...),(urlid2,wordlocation2_1,wordlocation2_2,wordlocation2_3...)] def locationscore(self,rows): locations=dict([(row[0],1000000) for row in rows]) for row in rows: loc=sum(row[1:]) #计算每个链接的单词位置总和,越小说明越靠前 if loc<locations[row[0]]: #记录每个链接最小的一种位置组合 locations[row[0]]=loc return self.normalizescores(locations,smallIsBetter=1)
第2个排名算法:根据单词频度进行评价的函数
# 根据单词频度进行评价的函数 # rows是[(urlid1,wordlocation1_1,wordlocation1_2,wordlocation1_3...),(urlid2,wordlocation2_1,wordlocation2_2,wordlocation2_3...)] def frequencyscore(self,rows): counts=dict([(row[0],0) for row in rows]) for row in rows: counts[row[0]]+=1 #统计每个链接出现的组合数目。 每个链接只要有一种位置组合就会保存一个元组。所以链接所拥有的组合数,能一定程度上表示单词出现的多少。 return self.normalizescores(counts)
第3个排名算法:根据单词距离进行评价的函数
# 根据单词距离进行评价的函数。 # rows是[(urlid1,wordlocation1_1,wordlocation1_2,wordlocation1_3...),(urlid2,wordlocation2_1,wordlocation2_2,wordlocation2_3...)] def distancescore(self,rows): # 如果仅查询了一个单词,则得分都一样 if len(rows[0])<=2: return dict([(row[0],1.0) for row in rows]) # 初始化字典,并填入一个很大的值 mindistance=dict([(row[0],1000000) for row in rows]) for row in rows: dist=sum([abs(row[i]-row[i-1]) for i in range(2,len(row))]) # 计算每种组合中每个单词之间的距离 if dist<mindistance[row[0]]: # 计算每个链接所有组合的距离。并为每个链接记录最小的距离 mindistance[row[0]]=dist return self.normalizescores(mindistance,smallIsBetter=1)
1.5 建立web交互
本文链接:http://www.wstdnwx.com/?id=588 转载需授权!
目录 返回
首页